Why Accurate Business Pricing Matters
Setting the right price when selling your business is crucial to attracting serious buyers and ensuring a smooth transaction. An overpriced business may scare away potential buyers, while underpricing can lead to significant financial loss. Understanding the factors involved in business valuation can help sellers achieve the best possible outcome and avoid common pitfalls.

Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or selling your first business, knowing how to price a business for sale is essential. This comprehensive guide covers the proven steps, methods, and expert insights you need to confidently navigate the valuation process and maximize your business’s value.
Step 1: Prepare Your Financial Statements
Before you can begin valuing your business, you must have clear and accurate financial records. Detailed statements demonstrate the health of your business and increase buyer confidence. Well-organized financials also make the valuation process more straightforward and credible.
- Profit and Loss Statements (P&L): Show revenues, expenses, and net income over the past 3-5 years.
- Balance Sheets: Outline assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity.
- Tax Returns: Provide additional verification and often required by lenders or buyers.
Maintaining clean financials not only helps with pricing but also streamlines due diligence, reducing the risk of delays or renegotiations later on.
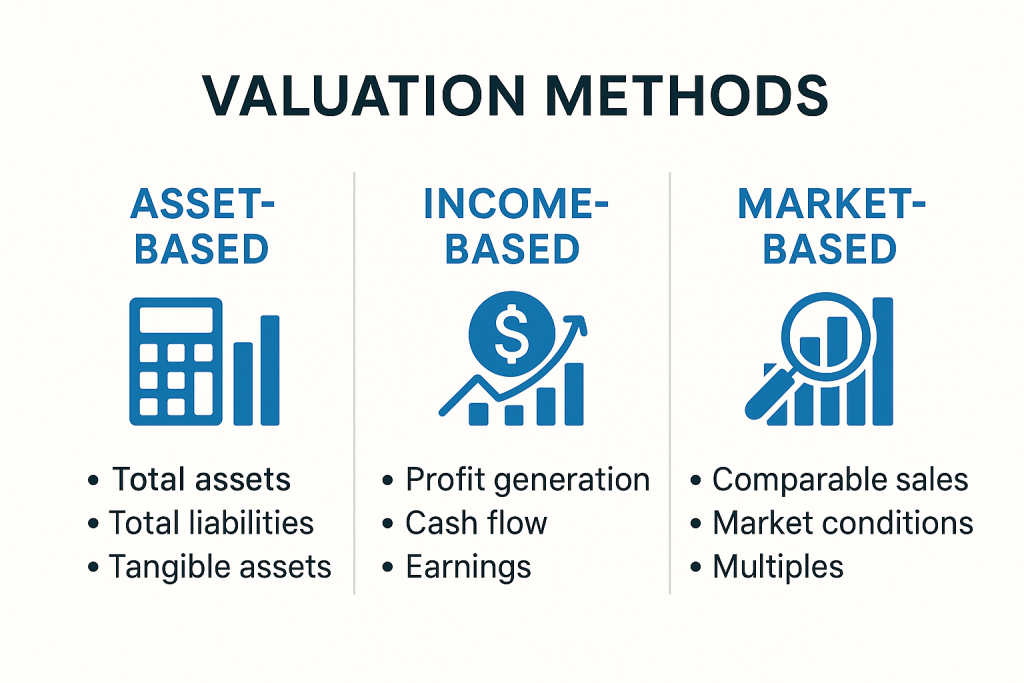
Step 2: Understand Key Valuation Methods
There are several proven methods for pricing a business, each designed to fit different types of businesses and industries. Using multiple methods can provide a more accurate picture of your company’s worth.
Asset-Based Valuation
Asset-based valuation calculates the value of your business based on total assets minus total liabilities. This approach works best for companies with significant tangible assets like real estate, equipment, or inventory. However, it may undervalue businesses with strong brand identity or intellectual property.
Income-Based Valuation
This method focuses on the business’s ability to generate profit. The most common approach is the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method, which estimates future cash flows and discounts them to present value. Alternatively, the Capitalization of Earnings method divides expected earnings by a capitalization rate to determine value. Both are ideal for profitable, stable businesses.
Market-Based Valuation
Market-based valuation compares your business to similar companies that have sold recently. By analyzing sale prices and key metrics like revenue or EBITDA multiples, you can estimate a fair market value. This method is highly effective in industries with abundant sale data and benchmarks.
Step 3: Normalize Your Earnings
Buyers want to understand the true earning potential of your business. Normalizing earnings involves adjusting your financial statements to account for non-recurring expenses, owner compensation, and discretionary spending. This process reveals the actual cash flow that a new owner can expect.
- Add-backs: Reimbursements for personal expenses run through the business, one-time costs, or owner’s salary above market rates.
- Adjustments: Remove any unusual, non-operational, or exceptional income or expenses.
Accurate normalization increases buyer trust and helps justify your asking price, especially if your discretionary expenses were unusually high or if you drew an above-average salary.
Step 4: Assess Market Trends and Comparable Sales
Market conditions can dramatically impact your business’s value. Understanding current industry trends, demand, and recent sales of similar businesses allows you to position your company competitively.
- Industry Multiples: Research the average selling multiples for similar businesses in your sector, such as revenue or EBITDA multiples.
- Comparable Sales: Examine details of recently sold businesses, including sale price, time on market, and deal structure.
Online databases, industry reports, and business brokers can provide valuable data to benchmark your business and set realistic expectations.
Step 5: Consider Intangible Assets and Unique Value Drivers
Beyond the numbers, intangible assets can add significant value to your business. Factors like a loyal customer base, brand reputation, intellectual property, and exclusive contracts can all boost your asking price.
Examples of Value Drivers
- Proprietary Technology: Custom software or patents that provide a market edge.
- Long-term Customer Contracts: Recurring revenue streams reduce buyer risk.
- Skilled Workforce: A talented, stable team adds operational continuity.
- Reputation and Brand: A well-known, respected brand increases perceived value.

Highlighting these unique attributes in your sales materials can help justify a premium price and set your business apart from competitors.
Step 6: Get a Professional Business Valuation
While you can estimate value using the methods above, a certified business valuation adds objectivity and credibility. Professional appraisers use industry standards, advanced analysis, and experience to provide an independent assessment.
- Certified Valuation Analysts (CVA): Recognized experts in business appraisal.
- Business Brokers: Offer practical insights and local market knowledge.
- Accountants and CPAs: Can provide detailed financial analysis and tax implications.
An independent valuation can be especially helpful for negotiations, obtaining financing, or if there are multiple owners with differing expectations.
Step 7: Set Your Asking Price Strategically
Once you have gathered all relevant data, it’s time to set your asking price. Consider the valuation, current market demand, and your own goals. Don’t forget to factor in negotiation room—most buyers expect to negotiate, so setting a slightly higher price can be advantageous.
Tips for Setting the Asking Price
- Avoid Emotional Pricing: Base your price on objective data, not personal attachment.
- Be Transparent: Be ready to justify your price with clear documentation and rationale.
- Be Flexible: Consider offering seller financing or creative deal structures to attract more buyers.
Remember, the goal is not only to achieve the highest possible price but also to close the sale smoothly and efficiently.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Pricing a Business for Sale
Many business owners make mistakes that can hinder the sale process or result in missed opportunities. Watch out for these common pitfalls:
- Ignoring market realities: Overpricing based on wishful thinking rather than data can lead to your business sitting unsold.
- Incomplete financials: Poor documentation erodes buyer confidence and can kill deals.
- Underestimating intangible value: Failing to consider brand, relationships, or proprietary assets can result in leaving money on the table.
- Not seeking expert advice: Skipping professional valuation or legal counsel may cost you much more in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions About Business Pricing
How long does it take to value a business?
The process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the business and the quality of the financial records. Engaging a professional can expedite the process and ensure accuracy.
What’s the most important factor in business valuation?
Consistent profitability and strong cash flow are usually the most critical factors, but industry, growth potential, and unique value drivers also play significant roles.
Should I use online business valuation tools?
Online calculators can provide a ballpark estimate, but they rarely account for the full picture. For an important transaction like selling your business, a customized, professional valuation is always recommended.
Conclusion: Maximizing Value When Pricing Your Business for Sale
Learning how to price a business for sale is an essential skill for any owner looking to exit successfully. By preparing accurate financials, understanding valuation methods, and seeking professional guidance, you can confidently set a price that reflects your business’s true worth and attracts motivated buyers. Follow these 7 essential steps, avoid common mistakes, and you’ll be well on your way to a rewarding and profitable sale.


