Sleep is a critical pillar of health and wellbeing, yet millions of women struggle to get enough, high-quality rest. While general sleep recommendations exist for adults, recent scientific research highlights that women’s sleep requirements and challenges are unique. So, how much sleep do women really need? Let’s explore the science, the reasons behind gender differences in sleep, and practical tips to help women get the most rejuvenating rest possible.
Why Is Sleep Important for Women?
Sleep is essential for every system in the body, but it plays especially crucial roles for women. During sleep, the body repairs tissues, balances hormones, supports immune function, and consolidates memories. For women, adequate sleep is linked to:
- Hormonal regulation: Sleep helps balance female hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, which are vital for reproductive health, menstrual cycles, and mood stability.
- Mental health: Women are statistically more prone to anxiety and depression, both of which are impacted by sleep quality and duration.
- Heart health: Quality sleep helps maintain cardiovascular health, which is especially important as women age.
- Metabolism: Sleep deprivation can disrupt metabolism and appetite control, contributing to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Immune function: Getting enough sleep helps fight off infections and reduces inflammation.
How Much Sleep Do Women Need?
The National Sleep Foundation and other health organizations recommend that most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep per night. However, evidence suggests that women often need slightly more sleep than men — on average, about 20 minutes more per night.
Why Might Women Need More Sleep Than Men?
- Multitasking brains: Research shows that women’s brains are more active and engage in more multitasking during the day, which may increase the need for restorative sleep.
- Hormonal fluctuations: The female hormonal cycle, including menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can disrupt sleep patterns and increase the need for more restful sleep.
- Greater risk of insomnia: Women are up to 40% more likely than men to report insomnia and sleep difficulties, further increasing their sleep needs.
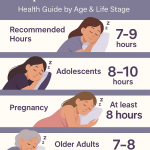
Sleep Recommendations by Age Group
Women’s sleep needs vary by age and life stage. Here’s a breakdown based on recommendations and research:
- Teenage girls (14–17 years): 8–10 hours per night.
- Young adults and adults (18–64 years): 7–9 hours per night. Some women may benefit from 9–10 hours, especially during periods of greater stress, physical activity, or hormonal changes.
- Older women (65+ years): 7–8 hours per night, although sleep may become lighter and more fragmented with age.
Life Stages Affecting Women’s Sleep Needs
Throughout life, women experience unique physiological changes that can impact both sleep duration and quality.
1. Menstruation and Sleep
Hormonal shifts during the menstrual cycle can cause sleep disturbances. Some women experience insomnia, night sweats, or increased fatigue prior to and during their periods.
2. Pregnancy
Pregnancy significantly affects sleep. Up to 80% of pregnant women report sleep issues, especially in the third trimester. The body’s changing shape, hormonal changes, frequent urination, and anxiety can all interfere with restful sleep. Experts recommend allowing for naps and extra sleep during pregnancy.
3. Perimenopause and Menopause
Hot flashes, night sweats, and hormonal fluctuations during perimenopause and menopause often cause insomnia and fragmented sleep. Women in this stage may need more time in bed to achieve the same restorative sleep as before.
Common Sleep Challenges for Women
Beyond biological factors, women frequently encounter sleep disruptors such as:
- Caregiving responsibilities (new mothers, family caregivers, etc.)
- Work-life balance and stress
- Chronic pain conditions (such as fibromyalgia or migraines)
- Mental health challenges (anxiety, depression, etc.)
Tips to Improve Sleep Quality for Women
While some sleep challenges are unavoidable, there are effective strategies women can use to optimize rest:
1. Prioritize a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate circadian rhythms and improves sleep quality.
2. Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
- Turn off screens at least 30 minutes before bed
- Practice relaxation techniques such as gentle yoga, meditation, or reading
- Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet
3. Manage Stress and Anxiety
Journaling, talking with friends, or seeking support from a therapist can help address the mental barriers to restful sleep.
4. Be Mindful of Diet and Exercise
- Avoid caffeine and heavy meals late in the day
- Engage in regular physical activity, but not too close to bedtime
5. Address Hormonal Changes
For women facing sleep disruptions due to menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, consult a healthcare provider about safe and effective strategies, which may include cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), hormone therapy, or natural remedies.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you consistently have difficulty falling or staying asleep, or if you never feel rested despite spending enough time in bed, it may be time to seek help. Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to numerous health risks, including depression, diabetes, and heart disease. Consult with a doctor or sleep specialist to rule out any underlying sleep disorders or medical conditions.
Conclusion: Listen to Your Body’s Sleep Needs
So, how much sleep do women need? While most women should aim for 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep per night, individual needs may vary. Women face unique biological and lifestyle factors that influence both the amount and the quality of sleep they require. By prioritizing rest and adopting healthy sleep habits, women can enhance their wellbeing, productivity, and overall health at every stage of life.